With technology trends constantly changing, we decided to ask our audience for their opinion. We wanted to know which trends they’re interested in, which trends they want to know more about in the coming year and how this could potentially influence business over the next 12 months:
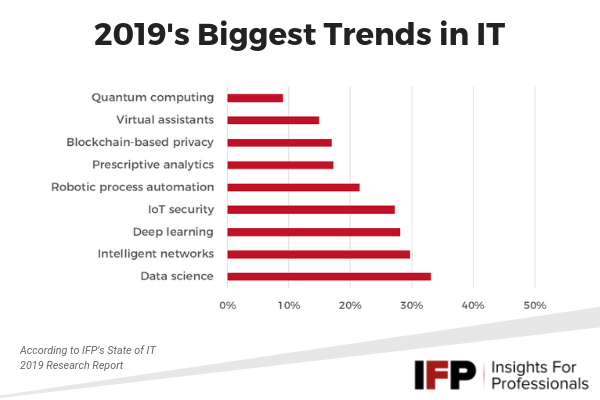
Here’s the biggest trends in order of popularity and how each one could impact businesses everywhere:
1. Data science (33%)
Businesses continue to drown in data, a problem that will only get worse for those not prepared to deal with it. Data scientists are the people to help make sense of it all, and provide business benefits from endless data streams, legacy databases and spreadsheets to unstructured data sources. By understanding and extracting value from data, these scientists use tools to help a business better understand trends and patterns. As big data flows become permanent fixtures from websites, Internet of Things devices and supply chains, all businesses need mastery of their data to succeed.
2. Intelligent networks (30%)
Modern business networks are now rarely limited to within the office, or across a WAN to regional divisions. New intelligent networks are spreading to the edge of the business at every function and datapoint. Edge computing delivers a decentralized connection from applications at the core to information coming from the edge, be it sensors, shipments, vending machines or other examples. These wider networks require additional security and analytic applications that can take advantage of the data for real-time intelligence.
That technology can be located at the edge to improve speed and efficiency dynamically changing how businesses view their networks.
3. Deep learning (28%)
Following on from data science comes the need to understand data, semantics and other tricky propositions using artificial intelligence. Deep learning is part of the machine learning field, focused on computational graphs, algorithms based on artificial neural networks to help machines understand information and produce actionable results for businesses to act on. The goal of machine learning is to help make business decisions easier in a world of big data and increasing time pressures.
4. IoT security (27%)
As with Intelligent Networks and IoT, new layers of security are required to protect the devices and secure data flows between networks that businesses will be increasingly reliant on. Businesses, smart city operators, supply chains and others need to prepare for attacks on IoT devices, denial of service outages and spoofing of devices or data. These threats require a joined-up business strategy using encryption, secure layers, validation and fallback positions to cope with loss of signal situations.
5. Robotic process automation (22%)
RPA continues to be a maturing technology among businesses, as part of digital transformations or digital business improvements. In basic terms, it helps businesses automate repetitive and low-value tasks, allowing workers to concentrate on value-added and more rewarding or creative tasks. RPA systems follow structured tasks, capturing data that a person previously would and feeding it into an application, from scanning in paper forms to responding to emails and making simple decisions based on the data it receives.
6. Prescriptive analytics (17%)
Prescriptive analytics is data analysis that offers a range of decision options based on the data. This provides a business with insights, opportunities or risk mitigation as the data comes in, instead of waiting for analysts to provide a lengthy report for C-level executives to mull over.
PA tools can provide quantified values of opportunity or risk, based on data and analysis, updated live as new data emerges, giving a growing picture of the optimal route to success.
The PA tool analyzes potential decisions, taking into consideration interactions between various elements within the data and other decisions within a process. Recommendations won’t be fool proof as with any tool, due to external influences and limits from the data, but could help businesses make better decisions faster.
7. Blockchain-based privacy (17%)
Blockchain vendors and proponents promise many things to businesses, but the key value that most end users seek is privacy. Blockchain can help protect privacy with its decentralized nature and the digital ledger, a visible public authority list that tracks, records and verifies as legitimate any transactions related to the data.
By having no central location that stores private data, and since blockchains can be linked to everything from photos to video, from databases to financial transactions, there is no single point of attack, making a blockchain system safer than current efforts. Privacy is assured as all users have their own private digital fingerprint of a cryptographic key to identify their transactions as genuine.
8. Virtual assistants (15%)
The evolution of virtual assistants from the smart home to the business is in full swing. Early use cases have moved on from virtual assistants acting as transcribers, note takers and dictaphones to providing business information, meeting reminders and messaging services. Virtual assistants will get rapidly smarter as they have access to more business information, helping teams meet, discuss and resolve problems, track productivity, and locate and provide useful information for each worker, wherever they are.
9. Quantum computing (9%)
Quantum computers are real hardware that is evolving rapidly to improve their computational power. Within a quantum computer lies a chip loaded with Qubits, replacing the traditional 1 or 0 of typical binary computers with both states at once, allowing faster computation of complex problems. While IBM has a chip with 50 qubits, Google’s new Bristlecone quantum chip packs in 72 quantum bits while Rigetti plans a 128-qubit chip that, when available to scientists and enterprises, will be able to calculate trillions of operations per second.
Access the latest business knowledge in IT
Get Access







Comments
Join the conversation...